✔️ Understanding Turpentine Oil for Safety Precautions and Guidelines.
In the 🌍 world of natural remedies and herbal extracts, understanding turpentine oil, stands as a potent substance with immense potential. Derived from the resin of pine trees, this essential oil has been used for various purposes throughout history. However, it is important to understand that turpentine oil should be handled with care due to its potentially harmful nature. In this article, we will delve into the safety precautions and guidelines that one should follow when using turpentine oil.
Many people are unaware of the precautions required when working with this volatile and flammable oil. Mishandling turpentine can lead to respiratory issues, skin irritation, poisoning, or even fire hazards. Therefore, understanding its nature, potential dangers, and safe handling practices is essential.
This blog post provides a comprehensive guide to understanding turpentine oil, its uses, associated risks, and the safety precautions and guidelines you must follow to ensure safe handling and application.
👉 What is Turpentine Oil?
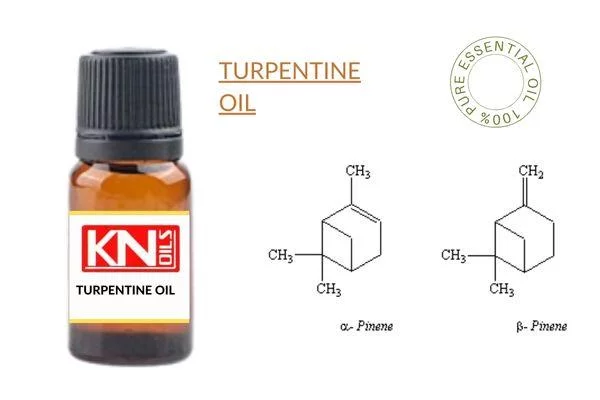
Turpentine oil, also known as spirit of turpentine or oil of turpentine, is a volatile essential oil consisting of numerous compounds extracted through the steam distillation of resins obtained from various species of pine trees. The resulting oil possesses a distinct aroma and has been widely adopted across industries such as ✔️medicine, ✔️paint solvents, and even as a ✔️traditional remedy. Its composition includes substances like ✔️alpha-pinene, ✔️beta-pinene,✔️ camphene, and ✔️other terpenes.
Safety Precautions When Handling Turpentine Oil
To ensure safe usage, it’s essential to follow strict guidelines when working with turpentine oil.
1. Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
-
Gloves: Always wear chemical-resistant gloves (e.g., nitrile or neoprene) to prevent skin contact.
-
Goggles: Use safety goggles to protect your eyes from accidental splashes.
-
Respiratory Protection: If working in poorly ventilated areas, wear a respirator mask designed for organic vapors.
-
Protective Clothing: Wear long sleeves and an apron to reduce the risk of skin exposure.
2. Proper Ventilation
-
Always handle turpentine in a well-ventilated space.
-
If indoors, use exhaust fans or open windows to disperse vapors.
-
Avoid confined areas where fumes can accumulate.
3. Storage Guidelines
-
Store turpentine in tightly sealed containers made of glass or metal.
-
Keep containers in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, away from direct sunlight or heat sources.
-
Label all containers clearly to avoid accidental misuse.
-
Do not store near oxidizing agents, acids, or open flames.
4. Handling Precautions
-
Never use turpentine near open flames, sparks, or smoking areas.
-
Avoid eating, drinking, or smoking while handling turpentine.
-
Always wash your hands thoroughly after use.
5. Safe Disposal
-
Do not pour turpentine down drains or into the soil.
-
Collect used or leftover turpentine in a sealed container.
-
Dispose of it at designated hazardous waste collection centers.
First Aid Measures for Turpentine Exposure
Despite taking precautions, accidents can happen. Here’s what to do in case of exposure:
-
Inhalation
-
Move the person to fresh air immediately.
-
Loosen tight clothing and keep them calm.
-
Seek medical attention if breathing difficulties persist.
-
-
Skin Contact
-
Remove contaminated clothing.
-
Wash affected skin thoroughly with soap and water.
-
Apply a soothing lotion if irritation continues.
-
Consult a doctor if burns or rashes develop.
-
-
Eye Contact
-
Rinse eyes with clean, lukewarm water for at least 15 minutes.
-
Do not rub the eyes.
-
Seek medical help immediately.
-
-
Ingestion
-
Do not induce vomiting, as it may cause aspiration into the lungs.
-
Rinse the mouth with water.
-
Call emergency medical services immediately.
-
Turpentine Oil in Traditional Medicine: A Word of Caution
In traditional practices, turpentine oil has been used in small amounts as a remedy for coughs, colds, and pain relief. However, modern medical experts strongly discourage self-medication with turpentine oil due to its toxicity and unpredictable effects.
-
Some old remedies involve inhaling vapors or applying diluted oil externally, but these methods pose significant risks.
-
Ingesting turpentine can cause poisoning, organ damage, and even death.
Safer alternatives such as eucalyptus oil, tea tree oil, or peppermint oil are now widely recommended for respiratory and pain-relief purposes.
Workplace Safety and Regulations
Industries that use turpentine must follow strict safety protocols:
-
Occupational Safety Standards
-
OSHA (Occupational Safety and Health Administration) sets exposure limits for turpentine fumes.
-
Employers must monitor air quality and provide PPE for workers.
-
-
Training and Awareness
-
Workers should be trained to handle turpentine safely.
-
Emergency procedures for spills, fires, and exposures must be in place.
-
-
Fire Safety
-
Keep fire extinguishers rated for chemical fires nearby.
-
Ensure proper grounding of containers to prevent static sparks.
-
Eco-Friendly Alternatives to Turpentine
Given the environmental and health concerns, many industries and consumers are turning to safer substitutes:
-
Citrus-based solvents – Derived from orange peels, effective and less toxic.
-
Mineral spirits – Less volatile but still requires precautions.
-
Water-based cleaners and paints – Environmentally friendly and safer to handle.
Choosing alternatives can significantly reduce health risks while maintaining efficiency.
Best Practices for Home Use
For those who may use turpentine at home (e.g., artists, woodworkers), following these practices is essential:
-
Always work in a garage, workshop, or open outdoor space.
-
Keep a fire extinguisher nearby.
-
Use only small quantities at a time to minimize risk.
-
Replace turpentine-soaked rags with safer substitutes like odorless mineral spirits or citrus cleaners.
👉 Handling Turpentine Oil in Various Settings
While turpentine oil finds applications in both industrial and domestic settings, it is essential to understand the specific safety measures required in each scenario.
👉 Household Use
- Proper Storage: Store turpentine oil in a dedicated, tightly sealed container, away from the reach of children and pets. Make sure it is kept in a cool and dry place, preventing exposure to sunlight.
- Dilution: Prior to use, diluting turpentine oil with a carrier oil is recommended to reduce its potency. This helps prevent any skin irritations or allergic reactions that may arise from direct application.
👉 Industrial Use
- Professional Guidance: In an industrial setting, it is crucial to consult with a trained professional who can guide you on the appropriate handling, storage, and usage of turpentine oil. They can also provide insights on safety protocols specific to the industry.
- Proper Disposal: Dispose of used turpentine oil following the regulations set by local environmental authorities. Improper disposal can lead to ecological damage, so it is important to adhere to established guidelines.
Conclusion
Turpentine oil remains a valuable substance in art, industry, and history, but it comes with serious risks that cannot be ignored. Its flammable, toxic, and volatile nature demands respect and careful handling.
By understanding its properties and following proper safety precautions and guidelines, individuals and industries can reduce health hazards and environmental impacts. Whether you are an artist, woodworker, or simply curious about traditional remedies, always remember: safety first when dealing with turpentine oil.
Safer alternatives are now widely available, and for most household or medical purposes, it’s best to opt for less hazardous options. Knowledge, caution, and responsibility are the keys to ensuring safe interactions with turpentine oil
Kanha Nature Oils
For more information contact: info@aromatherapyoil.in
Mobile Number: 981080586